
Federal Office tests CMS security vulnerabilities
The Federal Office for {Security in Information Technology}(http://www.bsi.de), together with init AG and the Fraunhofer Institute, has examined several open source CMS for security vulnerabilities. The results of the study can be viewed here.
Typo3 and Joomla have the most vulnerabilities
In general, the systems are certified as having a good level of security for the basic systems. The extensions cause problems. For Drupal, for example, the vulnerabilities are broken down as follows: 4% for the basic software vs. 96% for the extensions. The proportion of code execution vulnerabilities is highest in Typo3 and Joomla. This allows hackers to execute malicious code on the target system. Other common vulnerabilities in all systems are cross-site scripting and SQL injection.
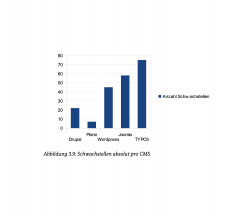
Weak points in the period 2010 - 2012
CMS extensions particularly incomplete
The BSI comes to the conclusion that there are generally gaps and that the CMS should therefore be configured correctly and security updates should be installed regularly. The greatest danger comes from the extensions, especially because these are patched less frequently.
Wordpress suffers the same fate as Microsoft
The popular CMS Wordpress has a similar fate to Microsoft. Whoever has the most users naturally also represents the largest and therefore most lucrative target group for hacker attacks and is therefore also the most dangerous. Nevertheless, it should also be mentioned that Wordpress patches security gaps that are found relatively quickly. However, these security patches must also be installed by the CMS admins and this is another part of the problem: anyone who has never been hacked or may not even know that the system is already being misused as a bot unnoticed will naturally not see the urgency in this.